A credit rating is a three-digit number utilized by lenders to evaluate your creditworthiness, that’s, how likely you might be to repay borrowed money on time.
Lenders use your credit rating to determine whether to approve you for brand spanking new loans or bank cards, and determine your credit limit and rate of interest. Landlords, employers and insurers may also use credit scores during their evaluation process.
Read on for a breakdown on how credit scores work and essentially the most common aspects that impact them.
How Do Credit Scores Work?
Credit scoring models analyze your credit reports from the three major credit monitoring agencies and assign a three-digit number between 300 and 850.
Each individual’s rating is calculated based on several aspects, reminiscent of payment history and credit utilization. The upper your rating, the less dangerous lenders consider you, so you’ll need more credit options and higher terms.
There are different credit scoring systems available, the preferred being FICO and VantageScore. Each model has several versions and a few are even tailored to specific lending industries, like mortgage and auto loans. Nonetheless, most creditors use FICO rating models.
How are credit scores calculated?
Credit scores are calculated using financial information that’s gathered by the key credit bureaus: Experian, Equifax and TransUnion.
These credit reporting agencies collect data from lenders to create a credit report for each consumer. This file will outline your credit history, including your payments and account balances.With this information, credit scoring models evaluate five major aspects: payment history, credit utilization, credit mix, credit inquiries and credit age.
How influential an element is depends upon the model utilized by a lender. Consequently, different scoring models can produce different credit scores, even in the event that they reference the identical credit report. Nonetheless, note that almost all models normally place more importance in your payment history and overall credit utilization.
Difference between credit scores and credit reports
Your credit rating will not be similar to your credit report. Credit scoring corporations use the data in your credit report to find out your credit rating. A credit report documents your credit history, and credit scoring models use it to find out your creditworthiness and, consequently, your rating.
Aspects that make up your credit rating
Each the FICO and VantageScore models use similar aspects to calculate scores. Nonetheless, each system weighs financial data a bit in another way. Here’s what you have to know:
| FICO | VantageScore 4.0 |
| Payment history (35%) | Payment history (41%) |
| Amounts owed (30%) | Age/mixture of credit (20%) |
| Length of credit history (15%) | Utilization (20%) |
| Latest credit (10%) | Latest Credit (11%) |
| Mixture of credit accounts (10%) | Balance (6%) |
| Available credit (2%) |
Payment history
Your payment history is the one most vital think about each scoring models. Paying your bills on time will increase your credit rating over time, while late payments of 30 days or more can knock off 100 points or more out of your rating and might be reflected in your report for as much as seven years.
Amount owed or utilization
Scoring models consider your credit utilization ratio, that’s, how much credit you utilize in comparison with your available total. To have a superb credit rating, experts recommend keeping your utilization at or below 30% — nonetheless, the lower the higher.
For instance, if you have got a card with a $10,000 credit limit, it is best to aim to make use of $3,000 or less every month. Nonetheless, take into account that this factor also takes into consideration the debt you’re carrying across multiple accounts. So if you have got three cards with a combined credit limit of $40,000, your outstanding balances shouldn’t exceed $12,000.
Age or length of credit history
One of the common credit rating myths is that no credit is healthier than weak credit. The reality is, nonetheless, that the older your accounts, the higher to your credit rating.
Creditors prefer borrowers with extensive credit histories since it lets them higher assess their creditworthiness. While there are not any suggestions to elongate the typical age of your credit faster, you possibly can avoid shortening it by keeping your oldest accounts open if possible.
Latest credit
Be mindful of how often you apply for brand spanking new loans or bank cards. If you have got too many recent accounts, lenders may consider you a dangerous borrower. This will also negatively impact your rating as credit applications generate a hard credit inquiry that may lower your rating by just a few points.
Credit mix
Having various kinds of accounts, reminiscent of a bank card and a automobile loan, may help boost your rating. Lenders wish to see a wide range of credit because it shows that you simply are in a position to pay back various kinds of debt reliably.
The right way to obtain a free credit rating
You need to use credit monitoring services, reminiscent of Credit Karma, to check your credit scores totally free. Nonetheless, these services often provide your VantageScore, and lenders use the FICO system rather more often. While each scoring models use similar aspects and scales, they still weigh your financial information a bit in another way.
You possibly can get your FICO rating by purchasing it directly from the FICO website. But some bank card corporations, like American Express, include it freed from charge as a perk for consumers.
What constitutes a superb credit rating?
The FICO scores range from from 300 to 850 points, where scores between 670 and 739 are considered good. Scores above that range are considered excellent or exceptional.
The VantageScore model has an analogous range and scores between 661 and 780 are good, while anything above that threshold is superb.
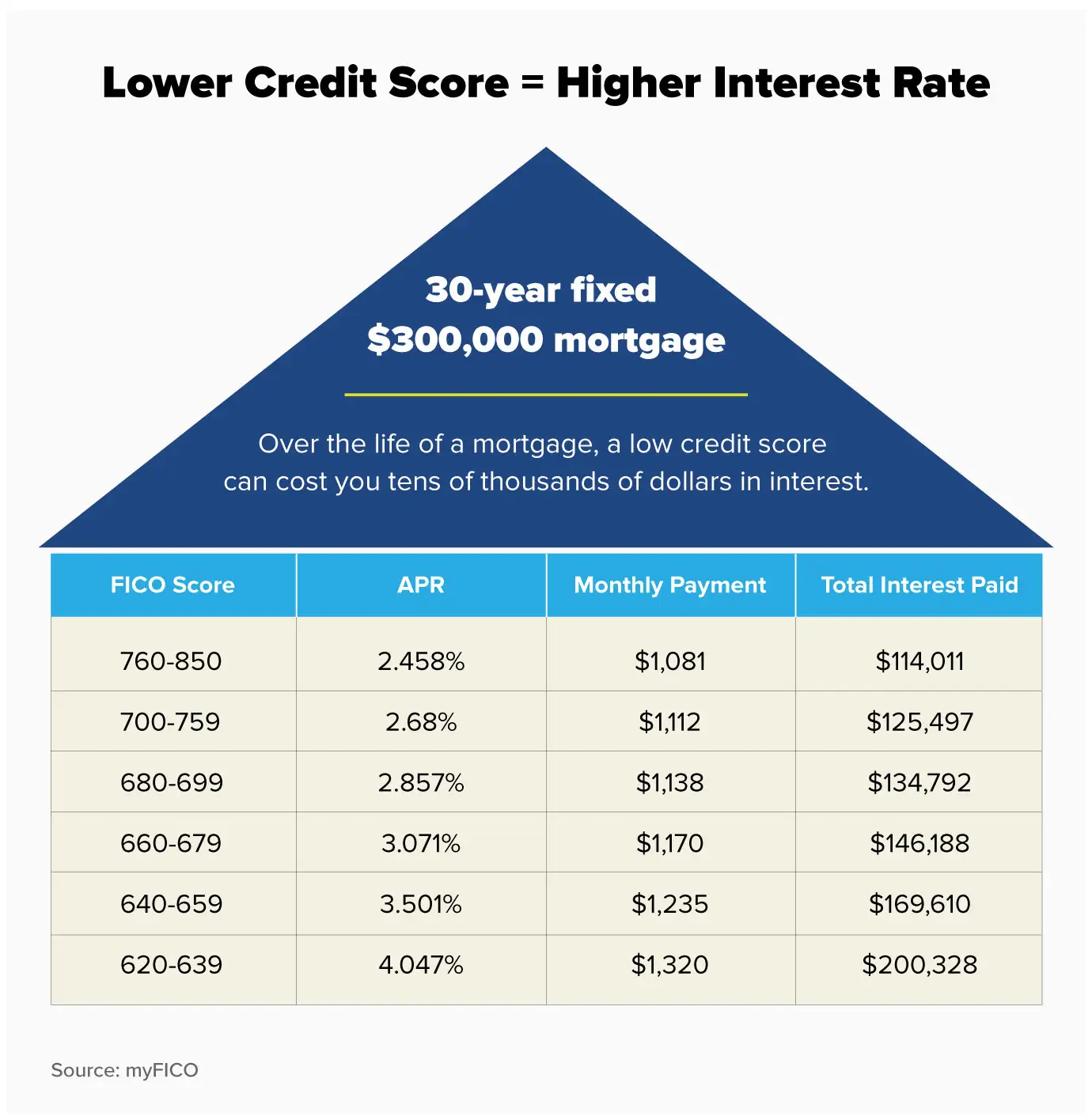
Good credit scores can increase your probabilities of approval while you apply for loans and bank cards. It’ll also increase how much you possibly can borrow when applying for a mortgage and other varieties of financing, like automobile loans, personal loans. Moreover, creditors will give you higher credit limits in your cards and higher rates of interest.

A superb rating may also be helpful while finding a house or apartment to rent. Many landlords and property managers use scores to guage your application since a superb credit rating can indicate you might be a responsible tenant that’s more likely to pay rent on time.
Sorts of credit accounts
Having various kinds of credit accounts in your report can improve your rating because it demonstrates that you could manage different sorts of debt. These are the 2 major types:
Installment loans
Installment loans refers to loans for a certain quantity of cash and with a hard and fast repayment schedule, for instance, student loans and mortgages. Installment loans require set monthly payments and missing them can result in late fees and your credit rating dropping.
Revolving credit
Any such account means that you can borrow as often as you’d like as much as a predetermined limit so long as you pay back a minimum of a few of the borrowed amount. As you pay down your balance, credit is once more available. An example of revolving credit can be a bank card or a house equity line.
Revolving credit accounts allow you to carry a balance over to the subsequent month. Nonetheless, which means interest accrues on the outstanding balance, making it grow month to month. To avoid these additional charges, it is best to attempt to pay the balance off in full every month.
What Can Lower Your Credit Rating?
Your credit rating can drop should you miss payments or max out your cards steadily.
These are a few of the most typical aspects that may lower your credit rating:
Bankruptcy
Filing for bankruptcy could make your credit rating drop by 200 points or more, and the filing might be reported in your report for as much as 10 years.
Foreclosure
In the event you are delinquent in your mortgage payments, the lender can foreclose the property, that’s, take ownership of it. Foreclosures can have a significantly negative impact and stay on the report for seven years.
High credit utilization ratio
Having a number of cards in good standing may help your rating, but should you’re using greater than 30% of your available credit, it will possibly start impacting it negatively.
Late payments
Only one late payment can lower your rating by 100 points or more, and remain in your credit report for as much as seven years — and the longer the payment is overdue, the greater the impact in your credit rating. For instance, a payment that’s 30 days late has a smaller impact than one which is 90 days late.
Credit inquiries
A credit inquiry (also often called a credit check or credit pull) happens when lenders have a look at your credit report.
There are two types:
A tough inquiry can lower your credit rating, but it surely’s only briefly and by just a few points. It’s more necessary to avoid having too many hard inquiries in your credit report inside a brief time frame since lenders might imagine you’re taking on an excessive amount of debt and consider it an indication of monetary instability.
| Hard inquiry | Soft inquiry |
| Tied to a proper loan or credit application | No formal loan or credit application linked to the inquiry |
| Lenders use it to simply accept or reject your application | Lenders and bank card issuers employ it to pre-approve candidates |
| Have to be authorized by you | Prospective employers and even phone corporations do soft checks as a part of your evaluation without your authorization |
| Remain in your report for as much as two years | Will not be reflected in your report |
| Too many can lower your overall rating | Are only visible to you and don’t impact your rating |
Common mistakes in your credit report
Once you check your credit report, be careful for common mistakes reminiscent of:
- Incorrectly reported late payments
- Accounts that belong to a different person
- Closed accounts reported as open
- Same account listed greater than once
In the event you spot considered one of these mistakes, they may simply be as a consequence of a reporting error out of your creditor or the reporting bureau. Nonetheless, note that it might indicate that you simply’re a victim of identity theft and another person is using your personal to use for credit.
The right way to fix credit report errors
Start by reviewing a duplicate of your credit report. You possibly can get weekly copies through AnnualCreditReport.com.
In the event you spot a mistake, reminiscent of an unauthorized hard inquiry, it is best to contact the credit bureau that generated the report back to request it remove the wrong item. Note that you could remove incorrect items out of your credit report totally free, but the method could be time consuming. In case your file has several errors, it is best to consider hiring a credit repair company.
It is best to also look into credit counseling should you want more personalized advice to enhance your financial situation. Nonprofit organizations reminiscent of the National Foundation for Credit Counseling (NFCC) can show you how to higher understand your funds and improve your rating over time.
Summary of Money’s Guide to What’s a Credit Rating?
A credit rating measures your creditworthiness and guides the creditor’s lending decisions on loan rates, terms and loan amounts. Credit scoring corporations use data out of your credit report — an in depth record of your borrowing history and behaviors — to calculate your credit rating.
You would like a superb credit rating to qualify for higher loan terms and rates of interest. A poor credit rating doesn’t disqualify you from borrowing money, but it surely does make it harder. Poor credit limits your lender options, raises your rates of interest, and might even disqualify your loan application.